
Ategenos Emerges from Stealth to Debut First-Ever SmartPatch Platform
Introducing the first scalable solution enabling real-time interventions for medication non-adherence

Introducing the first scalable solution enabling real-time interventions for medication non-adherence

Sweat does more than just cool down an overheating body. Measuring the chemical makeup of an individual’s sweat—specifically the levels of chloride, a chemical component of salt—can serve as an early warning system to help inform the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis, a genetic disease that damages the lungs and digestive system.

Researchers have developed an AI tool that can help doctors predict who might develop a potentially fatal heart condition, just from an ECG.
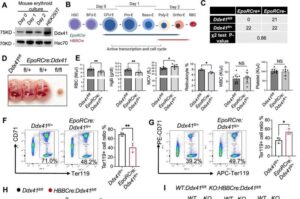
A new Northwestern Medicine study has revealed how a common inherited mutation disrupts red blood cell development and sparks inflammation that can lead to leukemia, according to findings published in Nature Communications.
How many times have you stared at a home COVID-19 test, waiting for the faint line that confirms an infection? Those home antigen tests often fail to detect a recent infection or one with no symptoms. A PCR test is more accurate, but it must be done by a medical lab and the results take days to deliver.

Having lived with an ALS diagnosis since 2018, Kate Nycz can tell you firsthand what it’s like to slowly lose motor function for basic tasks. “My arm can get to maybe 90 degrees, but then it fatigues and falls,” the 39-year-old said. “To eat or do a repetitive motion with my right hand, which was my dominant hand, is difficult. I’ve mainly become left-handed.”

Patients with some cancers, autoimmune diseases, and metabolic disorders often endure time-consuming intravenous (IV) infusions to receive the best protein-based treatments available. Because these protein therapeutics require high doses to be effective and are typically formulated at low concentrations to remain stable, IV infusion has been, until now, the only option.

Researchers from the University of California San Diego Sanford Stem Cell Institute have developed a novel method to stimulate and mature human brain organoids using graphene, a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon.
Researchers develop a fast-acting, cell-permeable protein system to control CRISPR-Cas9, reducing off-target effects and advancing gene therapy.

Cepheid announced that the test will be shipped to Canadian customers this month.