
Tasso-SNBL Secures Japanese Certification for Self-Collection Blood Kit
Breakthrough approval supports home-based testing and strengthens access to care

Breakthrough approval supports home-based testing and strengthens access to care
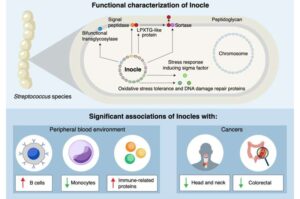
Researchers, including those at the University of Tokyo, have made a surprising discovery hiding in people’s mouths: Inocles, giant DNA elements that had previously escaped detection. These appear to play a central role in helping bacteria adapt to the constantly changing environment of the mouth.

An unusual therapy developed at The Jackson Laboratory (JAX) could change the way the world fights influenza, one of the deadliest infectious diseases. In a new study in Science Advances, researchers report that a cocktail of antibodies protected mice—including those with weakened immune systems—from nearly every strain of influenza tested, including avian and swine variants that pose pandemic threats.
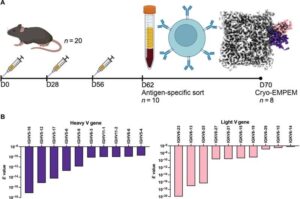
Scientists at Scripps Research have developed a novel method that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced imaging techniques to more accurately and efficiently identify therapeutic antibodies to treat infectious diseases.
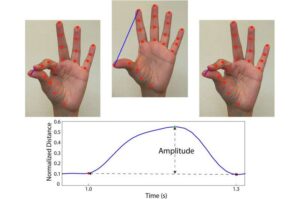
Early detection of even the slightest motor function changes can be critical to slowing the progression of Parkinson’s disease. Yet these subtle signs often go unnoticed. Now, UF researcher Diego L. Guarín, Ph.D., is harnessing AI to spot these subtle changes from video recordings before clinical symptoms become evident to the clinician’s eyes.
Maintaining an open airway is a critical priority in emergency medicine. Without the flow of oxygen, other emergency interventions can become ineffective at saving the patient’s life. However, creating this airway through endotracheal intubation is a difficult task for highly trained individuals and under the best of circumstances.

In a three‐year study involving more than 5,000 residents of Israel before and after the mass traumatic events of October 7, 2023, those who watched extensive media coverage of the attacks were found to be more likely to develop post‐traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).

A new method to keep human lymph node tissue alive and functioning outside the body for several days could give researchers a much clearer view of how our immune system responds to infections, vaccines and cancer, without the need for preclinical modeling or over-simplified laboratory models.

A quicker, cheaper MRI scan was just as accurate at diagnosing prostate cancer as the current 30–40 minute scan and should be rolled out to make MRI scans more accessible to men who need one, according to clinical trial results led by UCL, UCLH and the University of Birmingham.
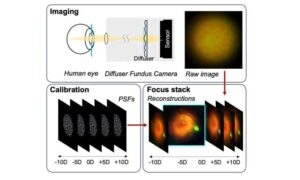
A team of researchers from Johns Hopkins University, Boston University, and collaborators has now demonstrated a new type of fundus camera that removes one of the main challenges: focusing. Instead of relying on mechanical adjustments of a lens, the system uses a special diffuser that captures 3D light information during imaging. With this data, a computer can reconstruct and refocus images after they are taken.