Medtronic gets FDA nod for Infuse bone graft in TLIF procedures
Medtronic (NYSE: MDT)+ announced today that it received FDA premarket approval (PMA) for the use of its Infuse bone graft in TLIF procedures.

Medtronic (NYSE: MDT)+ announced today that it received FDA premarket approval (PMA) for the use of its Infuse bone graft in TLIF procedures.
The system is intended for use in urgent care clinics, primary care settings, physician office laboratories, and pharmacies.

WESTFIELD, Ind., Feb. 17, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — Today, Portal Diabetes, Inc. (“Portal”) announced its receipt of the Breakthrough Device Designation by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its implantable insulin pump system called “Portal Pump,” and the start of a Phase 1 study on its proprietary temperature-stable insulin (“Portal Insulin”).
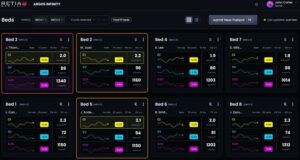
WHITE PLAINS, N.Y., Feb. 17, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — Retia Medical today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted 510(k) clearance for Argos Infinity™, the company’s cardiovascular intelligence software platform designed for high-risk surgical and critical care environments across health systems.

MURRIETA, Calif., Feb. 17, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — Copan Group announced today that PhenoMATRIX®, its automated image assessment software used with WASPLab® full laboratory automation, received FDA 510(k) clearance as a Class II device in the United States.

St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists, in collaboration with scientists at the Hopp Children’s Cancer Center Heidelberg (KiTZ), German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and other international centers, created Methylation-based Predictive Algorithm for CNS Tumors (M-PACT). M-PACT uses AI to sift through ctDNA in cerebrospinal fluid and molecularly classify tumors based on their DNA methylation pattern.
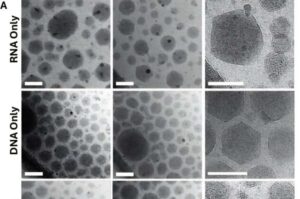
UCLA researchers have developed a lipid nanoparticle-based gene-editing approach capable of inserting an entire healthy gene into human airway cells, restoring key biological function in a laboratory model of cystic fibrosis and establishing a potential new path toward mutation-agnostic gene therapy for inherited lung diseases.
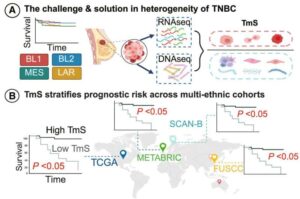
Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have developed a new computational approach designed to better account for changes in gene expression within tumors relative to their unique microenvironments. This approach outperformed current methods for predicting chemotherapy response in patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).