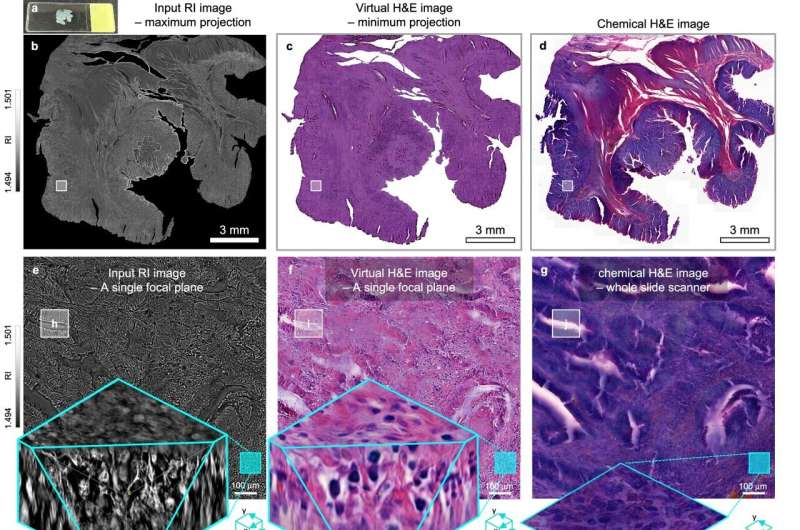
For over 200 years, conventional pathology has relied on observing cancer tissues under a microscope, a method that only shows specific cross-sections of the 3D cancer tissue. This has limited the ability to understand the three-dimensional connections and spatial arrangements between cells.
To overcome this, the research team utilized holotomography (HT), an advanced optical technology, to measure the 3D refractive index information of tissues. They then integrated an AI-based deep learning algorithm to successfully generate virtual Hematoxylin & Eosin images—the most widely used staining method for observing pathological tissues. Hematoxylin stains cell nuclei blue, and eosin stains cytoplasm pink.