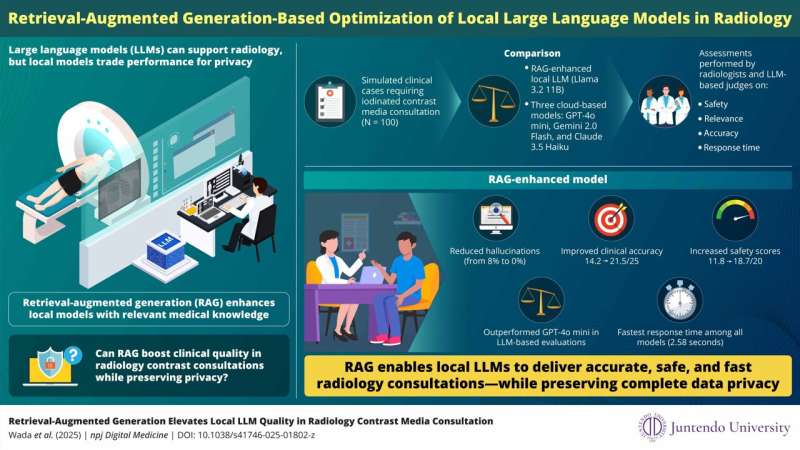
In a new study published online in npj Digital Medicine on July 2, 2025, a team of researchers led by Associate Professor Akihiko Wada from Juntendo University, Japan, demonstrated that retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), a technique that enables AI to consult trusted sources during response generation, can significantly improve the safety, accuracy, and speed of locally deployed large language models (LLMs) for radiology contrast media consultations.
The study was co-authored by Dr. Yuya Tanaka from The University of Tokyo, Dr. Mitsuo Nishizawa from Juntendo University Urayasu Hospital, and Professor Shigeki Aoki from Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine.
The team developed a RAG-enhanced version of a local language model and tested it on 100 simulated cases involving iodinated contrast media, a common component in computed tomography imaging. These consultations typically require real-time risk assessments based on factors like kidney function, allergies, and medication history. The enhanced model was compared to three leading cloud-based AIs—GPT-4o mini, Gemini 2.0 Flash, and Claude 3.5 Haiku—as well as its own baseline version, a standard LLM.