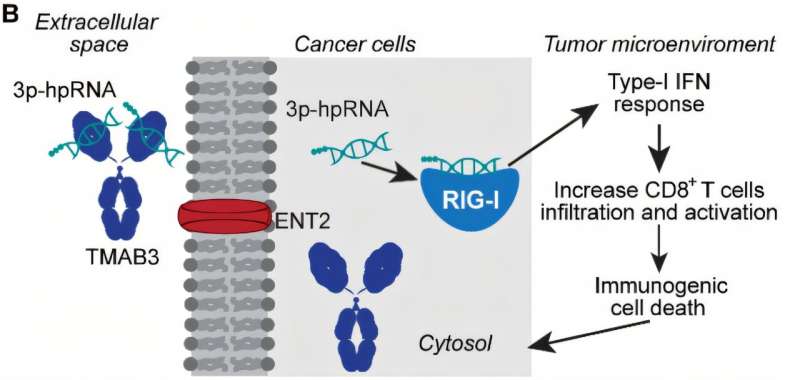
The study provides evidence that, once injected into the bloodstream, the antibody TMAB3, combined with a type of RNA that stimulates an innate immune reaction, can localize to tumors and penetrate and destroy stubborn diseased cells in pancreatic, brain, and skin cancers.
“Delivery of RNA-based therapies to tumors has been a challenge. Our finding that TMAB3 can form antibody/RNA complexes capable of delivering RNA payloads to tumors provides a new approach to overcome this challenge,” says Peter Glazer, senior author and Robert E. Hunter Professor of Therapeutic Radiology and Genetics at Yale School of Medicine (YSM).
In addition to Glazer and Yale first authors Elias Quijano, Ph.D.; Diana Martinez-Saucedo, Ph.D.; Zaira Ianniello, Ph.D.; and Natasha Pinto-Medici, Ph.D., there are 25 other contributors, most from Yale’s Department of Therapeutic Radiology and from the departments of genetics, molecular biophysics and biochemistry, biomedical engineering, pathology, and medical oncology and three from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.