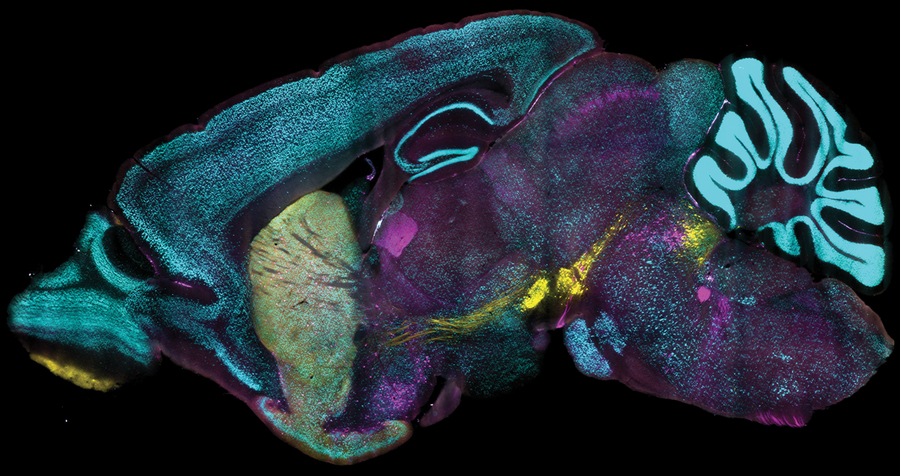
A new technology developed at MIT enables scientists to label proteins across millions of individual cells in fully intact 3D tissues with unprecedented speed, uniformity, and versatility. Using the technology, the team was able to richly label large tissue samples in a single day. In their new study in Nature Biotechnology, they also demonstrate that the ability to label proteins with antibodies at the single-cell level across large tissue samples can reveal insights left hidden by other widely used labeling methods.
Profiling the proteins that cells are making is a staple of studies in biology, neuroscience, and related fields because the proteins a cell is expressing at a given moment can reflect the functions the cell is trying to perform or its response to its circumstances, such as disease or treatment. As much as microscopy and labeling technologies have advanced, enabling innumerable discoveries, scientists have still lacked a reliable and practical way of tracking protein expression at the level of millions of densely packed individual cells in whole, 3D intact tissues. Often confined to thin tissue sections under slides, scientists therefore haven’t had tools to thoroughly appreciate cellular protein expression in the whole, connected systems in which it occurs.