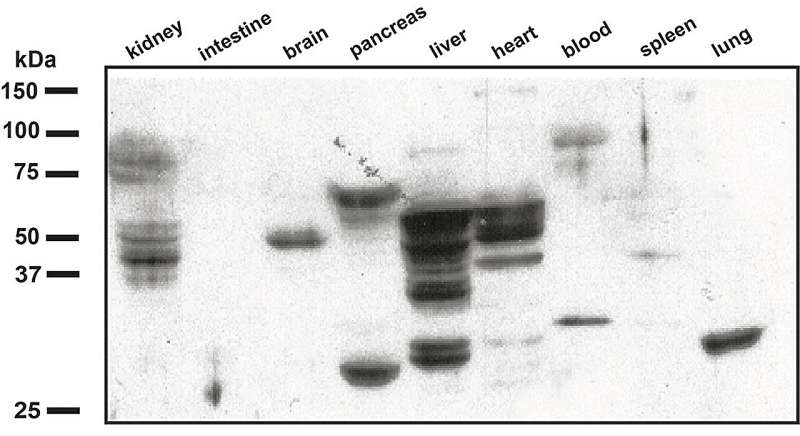
“This research opens up an amazing number of pathways for future studies,” said Greg Tochtrop, professor of chemistry at Case Western Reserve. “It will lead directly to better understanding inflammation and detecting diseases, as well as to discovering new drugs.”
The research, which Tochtrop led, is published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Inflammation leaves a trace
Tochtrop discovered that certain compounds formed from the interaction with reactive oxygen species (ROS)—highly reactive oxygen-containing chemicals that can damage DNA, proteins and lipids—react in a very unique way allowing detection using antibodies.