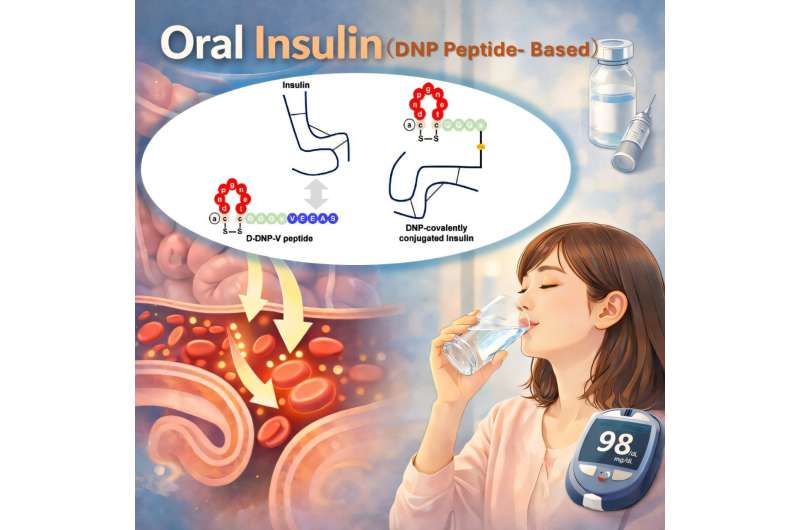
A research team at Kumamoto University, led by Associate Professor Shingo Ito, has developed a breakthrough drug-delivery platform using a small-intestine-permeable cyclic peptide known as the DNP peptide, enabling efficient oral delivery of insulin.
The study is published in Molecular Pharmaceutics.
Two complementary strategies for oral delivery
The researchers established two effective approaches to facilitate the intestinal absorption of insulin:
- Mixing method (interaction-based): A modified “D-DNP-V peptide” was simply mixed with zinc-stabilized insulin hexamers. Oral administration to multiple diabetes models—including chemically induced (STZ mice) and genetic (Kuma mice) models—rapidly reduced blood glucose levels to the normal range. Consistent glycemic control was maintained with once-daily dosing for three consecutive days.
- Conjugation method (covalent-based): Using click chemistry, the DNP peptide was directly conjugated to insulin to form a “DNP–insulin conjugate.” This produced glucose-lowering effects comparable to the mixing method, confirming active peptide-mediated intestinal transport.