These senescent cells are known to play a key role in wound repair and aging-related diseases, such as cancer and heart disease, so tracking their progress, researchers say, could lead to a better understanding of how tissues gradually lose their ability to regenerate over time or how they fuel disease. The tool could also provide insight into therapies for reversing the damage.
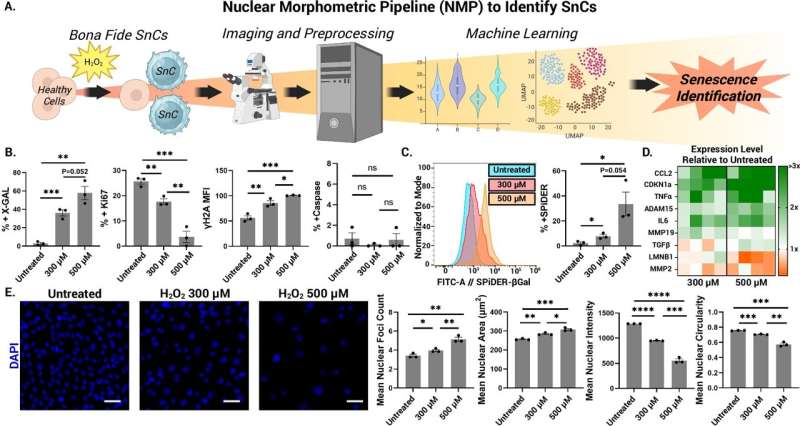
Led by NYU Langone Health Department of Orthopedic Surgery researchers, the study included training a computer system to help analyze animal cells damaged by increasing concentrations of chemicals over time to replicate human aging. Cells continuously confronted with environmental or biological stress are known to senesce, meaning they stop reproducing and start to release telltale molecules indicating that they have suffered injury.
Publishing in the journal Nature Communications online July 7, the researchers’ AI analysis revealed several measurable features connected to the cell’s control center (nucleus), that, when taken together, closely tracked with the degree of senescence in the tissue or group of cells. This included signs that the nucleus had expanded, had denser centers or foci, and had become less circular and more irregular in shape. Its genetic material also stained lighter than normal with standard chemical dyes.