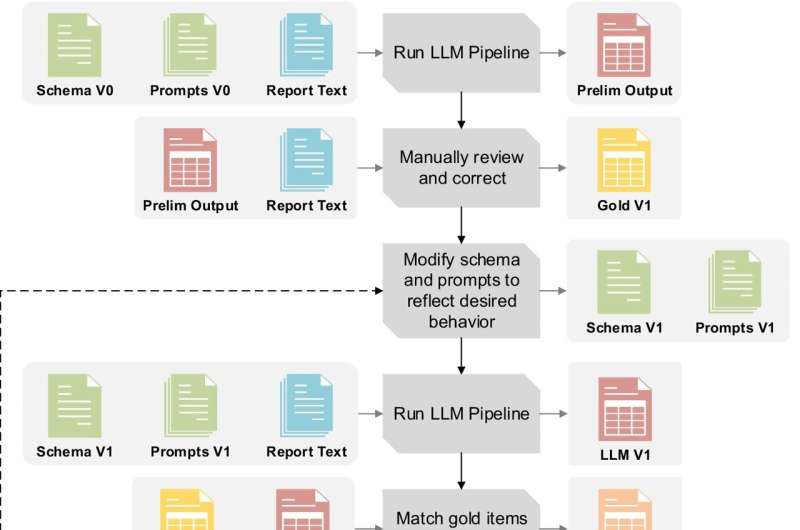
“Constructing highly detailed, accurate datasets from free-text medical records is extremely time-consuming, often requiring extensive manual chart review,” said study first author David Hein, M.S., Data Scientist in the Lyda Hill Department of Bioinformatics at UT Southwestern.
“Our study demonstrates one approach for creating AI-powered large language models (LLMs) that simplify the process of collecting and organizing medical data for analysis. By automating both data extraction and standardization through AI, we can make large-scale clinical research more efficient.”
To develop the pipeline, researchers used an AI-powered LLM to analyze more than 2,200 kidney cancer pathology reports to evaluate the model’s ability to recognize and categorize distinct types of tumors.
Through close collaboration with AI scientists, pathologists, clinicians, and statisticians, they refined the workflow through multiple rounds of testing, improving its handling of complex, nuanced information. Their findings were validated against existing electronic medical record (EMR) data to ensure reliability.