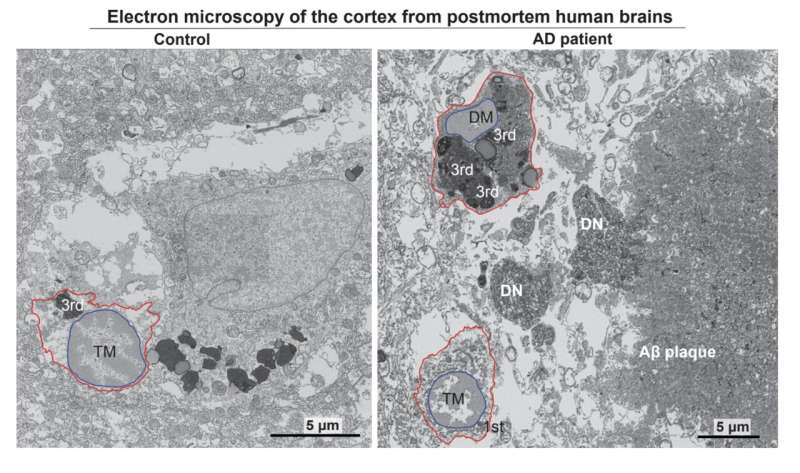
The study, published in the journal Neuron, highlights microglia, the brain’s primary immune cells, as central players in both the protective and harmful responses associated with the disease.
Microglia, often dubbed the brain’s first responders, are now recognized as a significant causal cell type in Alzheimer’s pathology. However, these cells play a double-edged role: some protect brain health, while others worsen neurodegeneration.
Understanding the functional differences between these microglial populations has been a research focus for Pinar Ayata, the study’s principal investigator and a professor with the CUNY ASRC Neuroscience Initiative and the CUNY Graduate Center’s Biology and Biochemistry programs.