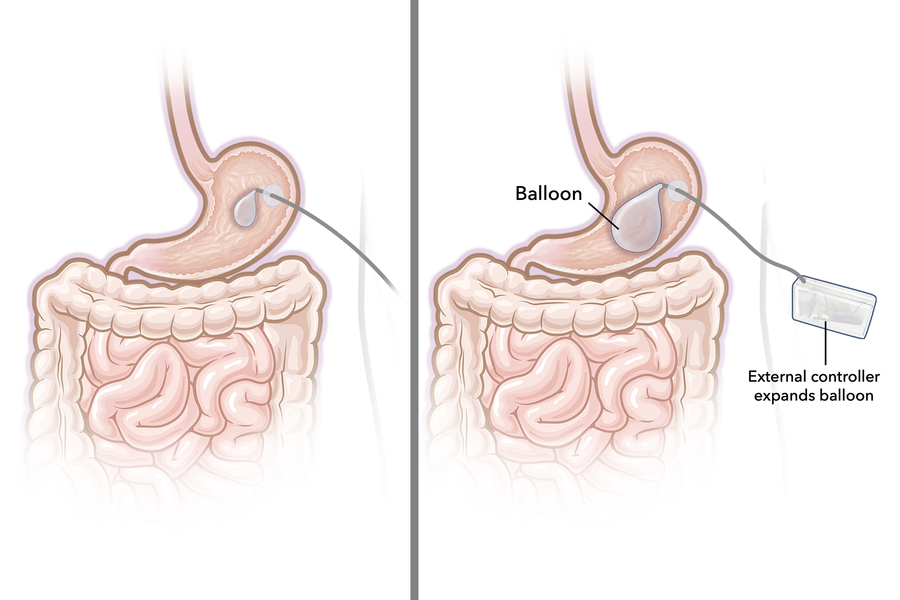
Gastric balloons — silicone balloons filled with air or saline and placed in the stomach — can help people lose weight by making them feel too full to overeat. However, this effect eventually can wear off as the stomach becomes used to the sensation of fullness.
To overcome that limitation, MIT engineers have designed a new type of gastric balloon that can be inflated and deflated as needed. In an animal study, they showed that inflating the balloon before a meal caused the animals to reduce their food intake by 60 percent.
This type of intervention could offer an alternative for people who don’t want to undergo more invasive treatments such as gastric bypass surgery, or people who don’t respond well to weight-loss drugs, the researchers say.
“The basic concept is we can have this balloon that is dynamic, so it would be inflated right before a meal and then you wouldn’t feel hungry. Then it would be deflated in between meals,” says Giovanni Traverso, an associate professor of mechanical engineering at MIT, a gastroenterologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and the senior author of the study.