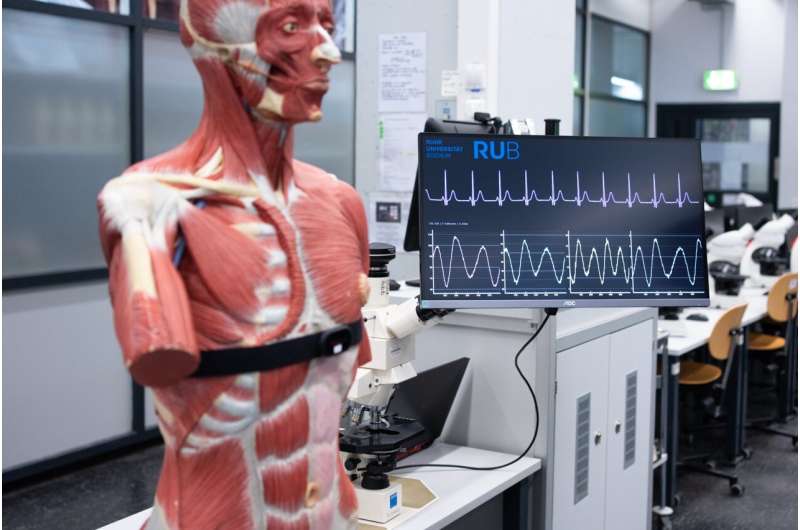
The AI can also account for subtle physiological signals such as changes in heart activity. This opens new doors for use in medical and care applications. The work is published in Frontiers in Digital Health.
Table and visualization of the data—no problem
For their experiment, the two researchers used a common device that measures heart rate variability via a chest strap. The data acquired from this were decoded, filtered, and condensed. In real time, the processed heart data were fed into the large language model GPT-4. In response to a corresponding prompt, the AI was able to correctly display the transmitted heart data in a table containing average values, minimum, maximum, and other information.