MedTech News
.................... by Andrew Celentano

Medtronic earns expanded FDA nod for deep brain stim
Medtronic (NYSE: MDT)+
announced that the FDA approved expanded labeling for its deep brain stimulation (DBS) offering.

Cardiawave wins CE mark for non-invasive aortic stenosis treatment
Cardiawave announced that it received CE mark approval for Valvosoft, its non-invasive therapeutic alternative for treating aortic stenosis (AS).

Axolotls Can Regrow a Key Organ From Scratch, Allowing Immune Cells to Fight Infections
Learn how axolotls are able to fully regenerate their thymus, a small organ that trains immune cells to fight infections.
IceCure Receives Notice of Patent Allowance in China for a Novel Cryogen Flow Control to Optimize Patient Cryoablation Outcomes
CAESAREA, Israel, Dec. 5, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — IceCure Medical Ltd. (NASDAQ: ICCM) (“IceCure”, “IceCure Medical” or the “Company”), developer of minimally-invasive cryoablation technology that destroys tumors by freezing as an option to surgical tumor removal, today announced it received a Notice of Allowance for a patent from the China National Intellectual Property Administration for its invention titled “Cryogen Flow Control” which relates to its next-generation XSense™ cryoablation system and probes.

Genetic variant may explain why some children with myocarditis develop heart failure
A genetic variant is likely putting some children suffering with myocarditis—inflammation of the heart muscle—at higher risk of developing heart failure, which can be fatal, according to a study published in Circulation Heart Failure.
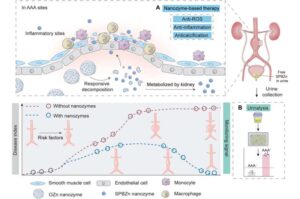
Ultrasmall theranostic nanozyme offers new hope for abdominal aortic aneurysm management
A team led by Professor Hui Wei, a pioneer in nanozyme research at Nanjing University, has unveiled an ultrasmall theranostic nanozyme with the potential to transform the diagnosis and treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)—a highly lethal vascular disease with limited therapeutic options.

Microglia replacement paves way for neurodegenerative disease therapies, moving from mice to humans in just 5 years
Tiny immune cells called microglia protect the central nervous system (CNS) in a multitude of ways: They provide innate immunity, shape neurodevelopment, maintain homeostasis and modulate neurological disorders. That functionality can be lost, however, when microglia acquire mutations.
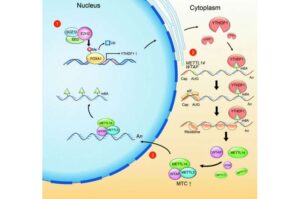
Exploring the link between RNA modification and prostate cancer growth
A Northwestern Medicine study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation has uncovered a connection between a well-known cancer-related protein and a major RNA modification process, which may inform new treatment strategies against prostate cancer.
