The work, published in npj Digital Medicine, demonstrates how artificial intelligence (AI) can unlock diagnostic value from images that would traditionally be considered unusable, reducing the cost and complexity of digital pathology without compromising diagnostic performance.
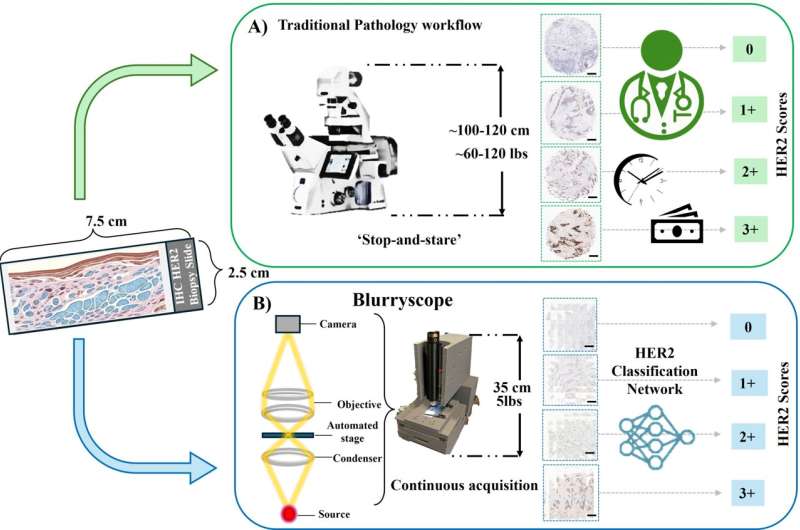
Digital pathology has become an indispensable part of modern cancer diagnostics, enabling precise evaluation of biomarkers such as HER2, a protein that plays a critical role in guiding treatment decisions for breast cancer patients. However, the high cost and large footprint of whole-slide imaging scanners have limited their widespread adoption, especially in clinics with constrained budgets or in resource-limited regions.
Conventional scanners can cost upwards of $100,000, and their large size makes them impractical for many laboratories. In contrast, the BlurryScope system can be built for less than $650, occupies only a 35 x 35 x 35 cm space, and weighs just 2.26 kg—making it portable, accessible, and affordable.