
Men lose their Y chromosome as they age: Scientists thought it didn’t matter—but now we’re learning more
New techniques to detect Y chromosome genes show frequent loss of the Y in tissues of older men.

New techniques to detect Y chromosome genes show frequent loss of the Y in tissues of older men.

For the first time ever, NTNU researchers have identified new characteristics of aggressive prostate cancer.
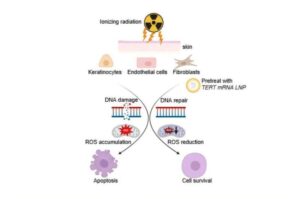
Researchers at Houston Methodist Research Institute have now discovered a promising new approach that can protect patients from radiation-induced skin damage during cancer treatment.

Genetic ancestry plays a key role in determining the behavior of head and neck tumors and may help explain why African-American patients survive for half as long as their counterparts of European ancestry, according to a new review study led by researchers from the University of Maryland School of Medicine’s (UMSOM) Institute for Genome Sciences (IGS) and the University of Maryland Greenebaum Comprehensive Cancer Center (UMGCCC).
Hydrocephalus is a life-threatening condition that occurs in about 1 in 1,000 newborns and is often treated with invasive surgery. Now, a new study offers hope of preventing hydrocephalus before it even occurs. The paper is published in the journal Molecular Therapy.
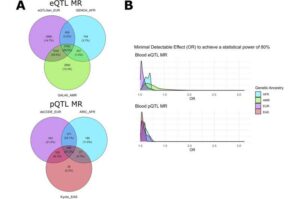
Numerous genetic studies have identified many risk variants for type 2 diabetes (T2D)—but which genes and proteins are actually involved in the disease mechanisms?
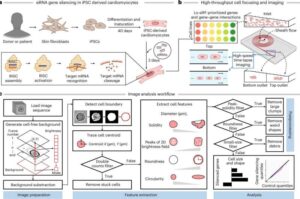
Euan Ashley’s lab explores the intricate interactions of gene variants. Tiny “typos,” or genetic mutations, can sneak into segments of DNA. Many of these are harmless, but some can cause health problems. Two or more genes can team up and change the outcome of a physical or molecular trait. This phenomenon, known as epistasis, occurs through complex interactions between genes that are functionally related—such as those that support protein creation.
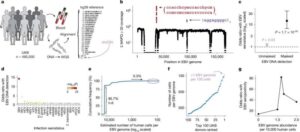
Baylor College of Medicine researchers are part of a collaborative research group with AstraZeneca and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center that have identified 22 genes which increase the risk of developing a range of chronic conditions following a common viral infection.

Gene-editing tools like CRISPR have unlocked new treatments for previously uncurable diseases. Now, researchers at the University of British Columbia are extending those possibilities to the skin for the first time.
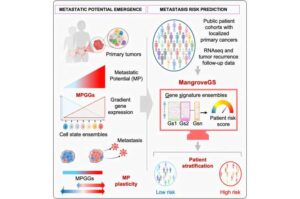
Why do some tumors spread while others remain localized? The mechanisms governing the metastatic potential of tumor cells remain largely unknown—yet understanding this is crucial for optimizing patient care.