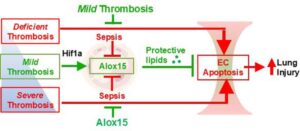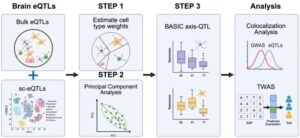
New technique maps genetic variants driving neurodegenerative disease risk
A team led by researchers from Penn State College of Medicine has developed a new method that substantially improves the ability to map the genetic variants that drive disease, particularly neurodegenerative diseases.