
Cytokinetics Wins FDA Approval, Clearing Way to Challenge BMS in Heart Disease Market
Stifel analysts said the label for cardiac myosin inhibitor Myqorzo is in line with their expectations and is differentiated compared with BMS’ Camzyos.

Stifel analysts said the label for cardiac myosin inhibitor Myqorzo is in line with their expectations and is differentiated compared with BMS’ Camzyos.

Abbott (NYSE: ABT)+
announced today that the FDA approved its Volt pulsed field ablation (PFA) system to treat patients with AFib.
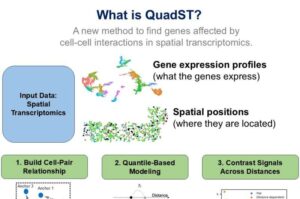
Scientists at Duke-NUS Medical School have developed two powerful computational tools that could transform how researchers study the “conversations” between cells inside the body. The tools, called sCCIgen and QuadST, help scientists understand both where cells are located in tissues and how they communicate through genetic activity and chemical signals.
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death in the U.S., second only to heart disease. But a new cancer treatment method from CU Boulder researchers uses sound waves to soften tumors and could be a potent tool against the disease.

Craif Inc. in Nagoya, Japan, working with Nagoya University’s Institute of Innovation for Future Society, has developed a urine-based biological aging clock. In validation of the method, predicted ages came within 4.4 years of chronological age on average.

A University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center study reveals how prostate cancer cells adapt their metabolism to thrive in bone tissue, offering a potential new treatment target for patients with advanced disease.
Australian researchers have discovered that the TAK1 gene helps cancer cells survive attack from the immune system, revealing a mechanism that may limit the effectiveness of immunotherapy treatments.
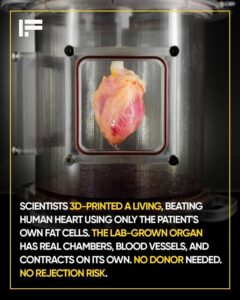
Researchers at Tel Aviv University achieved a medical milestone once thought impossible: creating a living, beating human heart using a patient’s own fat cells.

Zoll announced today that it launched its next-generation LifeVest wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) in the U.S.
Researchers have developed a new compact Raman imaging system that is sensitive enough to differentiate between tumor and normal tissue. The system offers a promising route to earlier cancer detection and to making molecular imaging more practical outside the lab.