“We show for the first time that light can be converted into cardiac stimulatory cues, with synthetic materials made of biomolecules,” said Herdeline Ann Ardoña, assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering. “This can be beneficial for downstream medical applications, such as in cardiac pacemaking technologies, or helping direct therapeutic patient-derived stem cells to better mimic adult heart cell features.”
The findings are reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The paper’s co-first authors are recent Ph.D. graduate Sujeung Lim, and Ze-Fan Yao, previous postdoctoral scholar in the Ardoña Research Group.
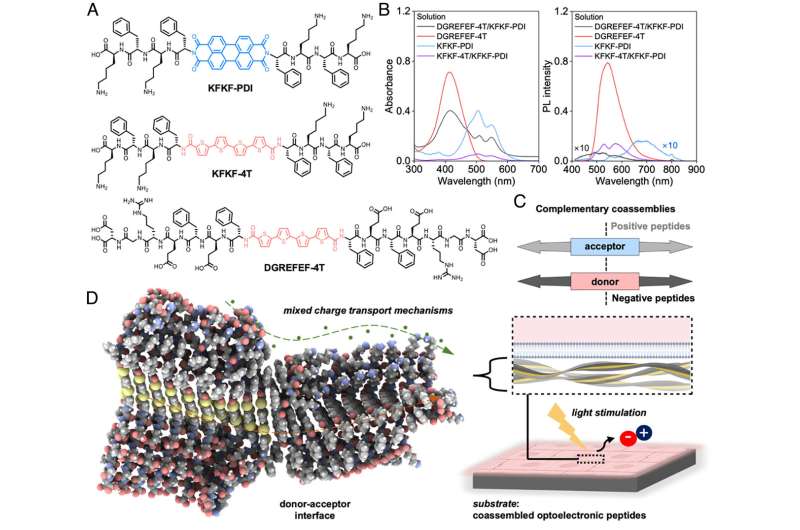
The researchers explain that several synthetic soft biomaterials already exist that are used to provide support in recreating heart tissues in a laboratory setting. However, many only offer passive support to growing tissue. This new material system provides both structural support and active signals initiated by light irradiation to deliver cues that impact cardiac behavior.