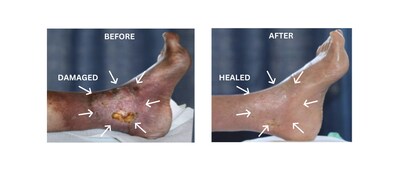
The study reports that tissue previously considered beyond recovery — and slated for surgical amputation — was able to stabilize and heal when peripheral neuropathy was directly addressed through a targeted nerve signaling intervention. These findings suggest that neuropathy plays a central, previously underappreciated role in determining whether damaged tissue can recover, rather than serving as a fixed, irreversible condition.
Peripheral neuropathy affects millions of patients worldwide and is commonly associated with diabetes, vascular disease, and trauma. Over time, progressive nerve dysfunction disrupts blood flow regulation, immune response, and cellular repair mechanisms — contributing to chronic tissue breakdown, recurrent wounds, loss of mobility, and, ultimately, amputation. Standard wound-care approaches largely focus on managing surface-level damage, infection, or moisture balance, without addressing the underlying nerve dysfunction that prevents tissue from repairing itself.