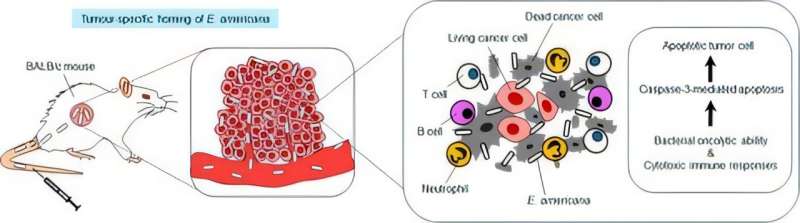
While the relationship between gut microbiota and cancer has attracted considerable attention in recent years, most approaches have focused on indirect methods such as microbiome modulation or fecal microbiota transplantation. In contrast, this study takes a completely different approach: isolating, culturing, and directly administering individual bacterial strains intravenously to attack tumors—representing an innovative therapeutic strategy.
The research team isolated a total of 45 bacterial strains from the intestines of Japanese tree frogs, Japanese fire belly newts (Cynops pyrrhogaster), and Japanese grass lizards (Takydromus tachydromoides). Through systematic screening, nine strains demonstrated antitumor effects, with E. americana exhibiting the most exceptional therapeutic efficacy.