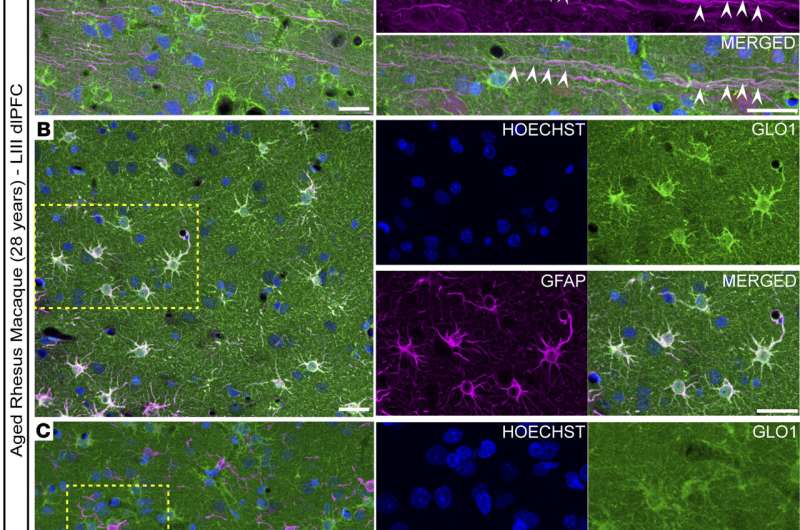
Glyoxalase 1 (GLO1) is a protein that plays an essential role in getting rid of toxic byproducts in cells. In the study, Yale School of Medicine (YSM) researchers discovered elevated GLO1 levels in the brains of animals with excessive levels of cellular calcium, finding that the brain increased GLO1 expression as a protective mechanism to mitigate the effects of the calcium dysregulation.
However, with advancing age, GLO1 activity declined, the researchers found, which may make the brain less resilient to neurodegeneration. The study could inform the development of therapeutics that target GLO1 and prevent neurodegeneration.
“We discovered how the brain itself deals with calcium leak and uses a resilience factor that erodes with age,” says Amy Arnsten, Ph.D., Albert E. Kent Professor of Neuroscience and the study’s co-principal investigator. “If we could keep this mechanism going, we’d be protecting the brain in a way that the brain itself has devised.”