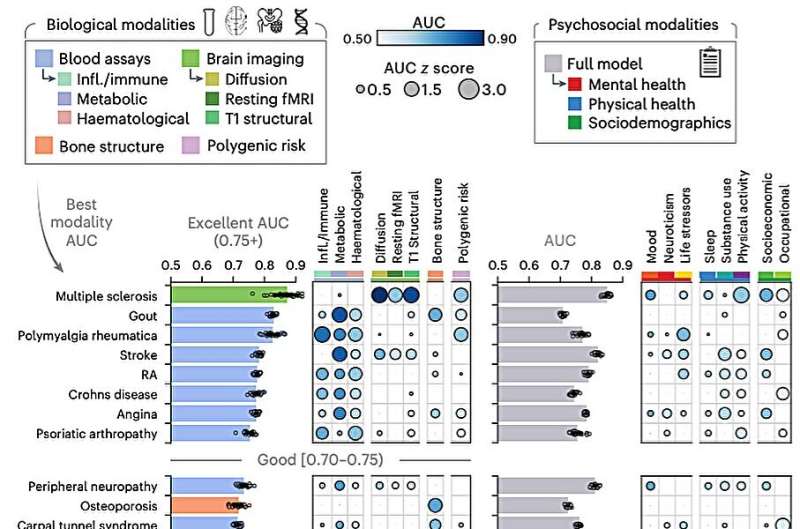
“Our study started as an effort to identify reliable brain-based biomarkers for chronic pain using data from the UK Biobank, the largest brain imaging cohort available,” Matt Fillingim, first author of the paper, told Medical Xpress. “We quickly found that these biomarkers could not reliably distinguish chronic pain from pain-free individuals.
“However, when applied to specific pain conditions like fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis, the biomarkers showed greater promise, prompting us to integrate additional psychosocial factors and diverse biological data (blood tests, bone imaging, genetics) to better understand chronic pain and its associated conditions.”