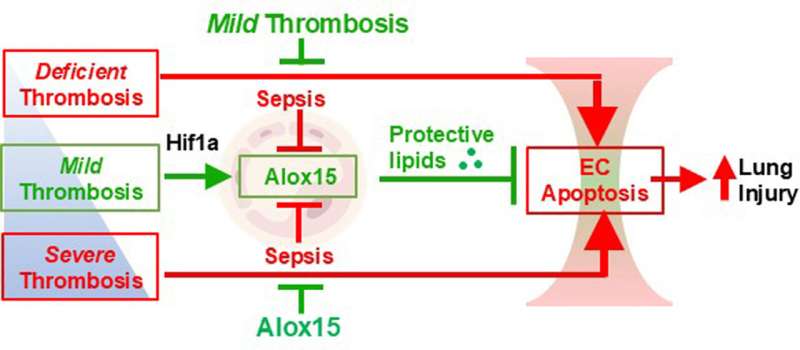
Sepsis, or infection causing uncontrolled inflammatory response and organ dysfunction, often results in acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Patients with sepsis-caused lung injury also commonly suffer from severe thrombosis, or blood clotting, but clinical trials of anticoagulant therapies in sepsis and ARDS patients have failed.
Despite improvements in supportive care, including mechanical ventilation and antibiotic therapy, there is currently no effective treatment for sepsis and ARDS, and mortality rates for patients with ARDS are still as high as 40%.