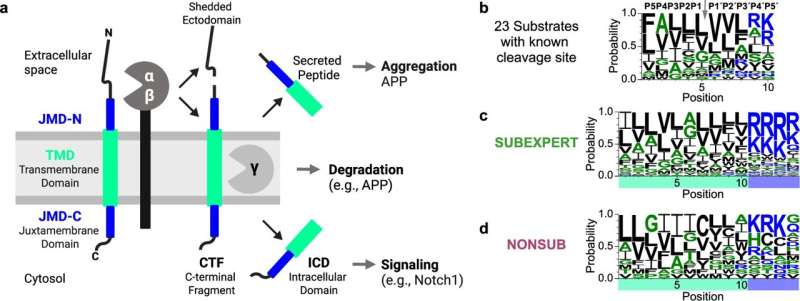
Their study, published in Nature Communications, introduces a methodology that decodes the enzyme’s recognition logic by bridging biochemistry with explainable artificial intelligence (AI). This novel approach could help to better understand the role of gamma-secretase in diseases and aid drug development.
Gamma-secretase is an enzyme belonging to the category of “proteases” that plays a key role in Alzheimer’s disease and cancer. It occurs in the membrane of numerous cells, including neurons, where—acting like a pair of scissors—it cleaves other membrane-bound proteins.
In the context of Alzheimer’s disease, this happens with the so-called amyloid precursor protein. However, the enzyme is versatile: It has more than 150 known targets, also referred to as “substrates.” Until now, the reason why gamma-secretase breaks down these particular molecules has been a mystery.