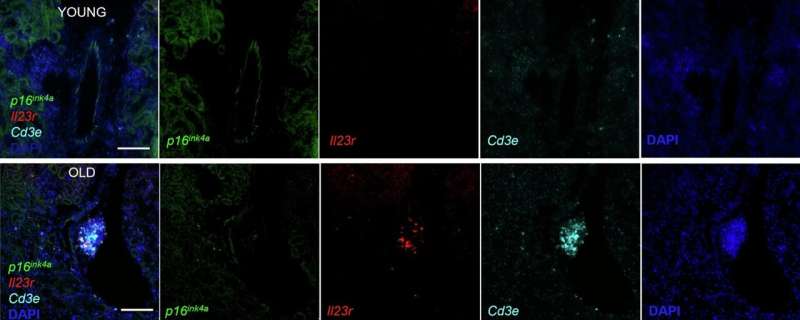
Cellular senescence occurs when cells stop dividing but do not trigger apoptosis mechanisms that would allow them to die naturally. Instead, they are stuck in a zombie-like state, where they still have the urge to feed and carry out metabolic activities, but with increasingly incoherent cell signaling and increased pro-inflammatory cytokine secretions.
Senescent cell activity has been linked to several age-related diseases, including those of the immune, cardiovascular, metabolic, pulmonary, musculoskeletal and neurological systems.
Scientists have been searching for a biomarker that reliably estimates the levels of active senescent cells in the body. If found, this biomarker could inform clinical interventions, potentially intervening before disease conditions present themselves.