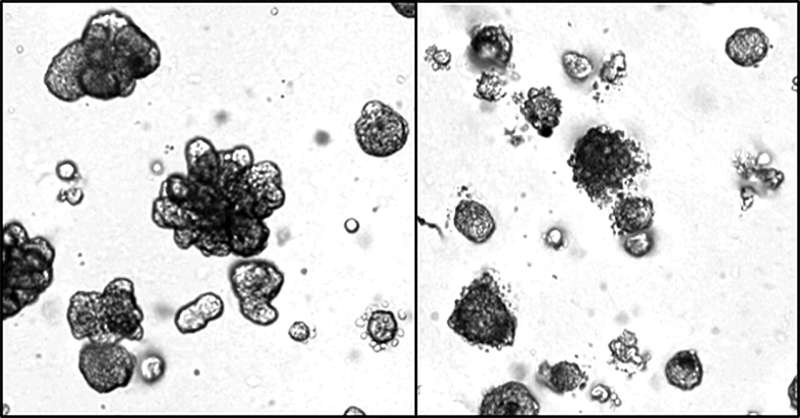
Their approach employs an antibody-drug conjugate—a delivery system that uses an antibody to identify cancer cells and deliver a highly potent chemotherapy directly into those cells without harming surrounding healthy tissue. Antibody-drug conjugates make it possible to use chemotherapy drugs that are too toxic to deliver on their own, offering a promising avenue for treating the most difficult cancers.
The research is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Why triple-negative breast cancer is challenging
In 2025, an estimated 316,950 women and 2,800 men will be diagnosed with invasive breast cancer. TNBC accounts for about 10–15% of all breast cancer cases, and it is widely considered the most difficult breast cancer subtype to treat. This is because TNBC tends to grow and spread more quickly than other forms of breast cancer, and it typically fails to respond to therapies that work in other subtypes, such as hormonal therapies.