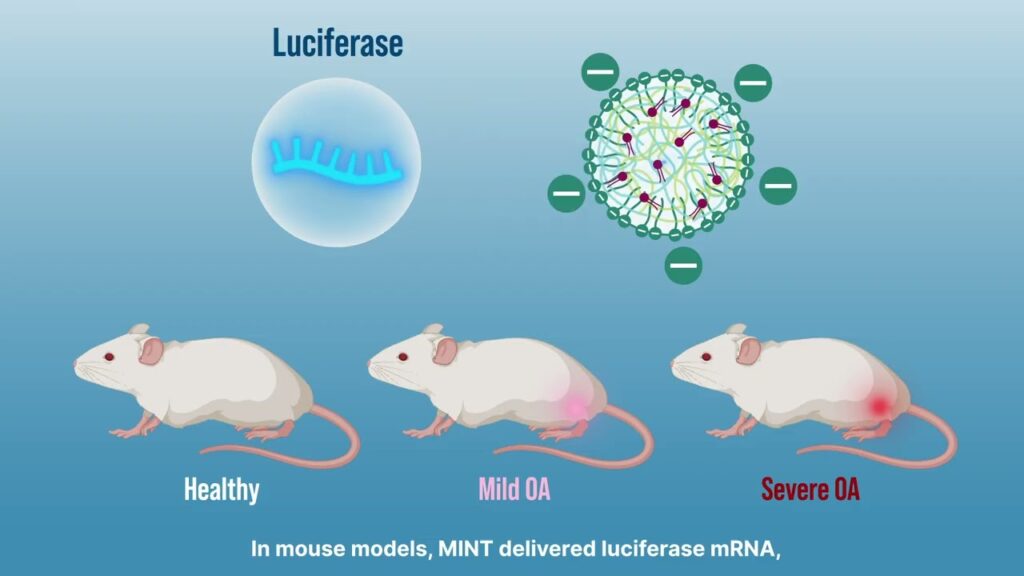
Intra-articular RNA therapeutics have shown promise in osteoarthritis (OA); however, maximizing their efficacy requires targeted delivery to degenerating cartilage within focal lesions. As OA progresses, cartilage degeneration worsens, necessitating disease-responsive targeting with enhanced delivery in advanced stages. Here we develop an anionic nanoparticle (NP) strategy for targeting glycosaminoglycan loss, a hallmark of OA’s progression that reduces cartilage’s negative charge. These NPs selectively diffuse and accumulate into matrix regions inversely correlated with glycosaminoglycan content owing to reduced electrostatic repulsion, a strategy we term ‘matrix inverse targeting’ (MINT).
In a mouse model of OA, intra-articular delivery of luciferase messenger RNA-loaded MINT NPs demonstrated disease-severity-responsive expression. Using this strategy, we delivered ghrelin mRNA, as ghrelin has shown chondroprotection properties previously. Ghrelin mRNA-loaded MINT NPs reduced cartilage degeneration, subchondral bone thickening and nociceptive pain. Our findings highlight the potential of ghrelin mRNA delivery as a disease-modifying therapy for OA and the platform’s potential for lesion-targeted RNA delivery responsive to disease severity.