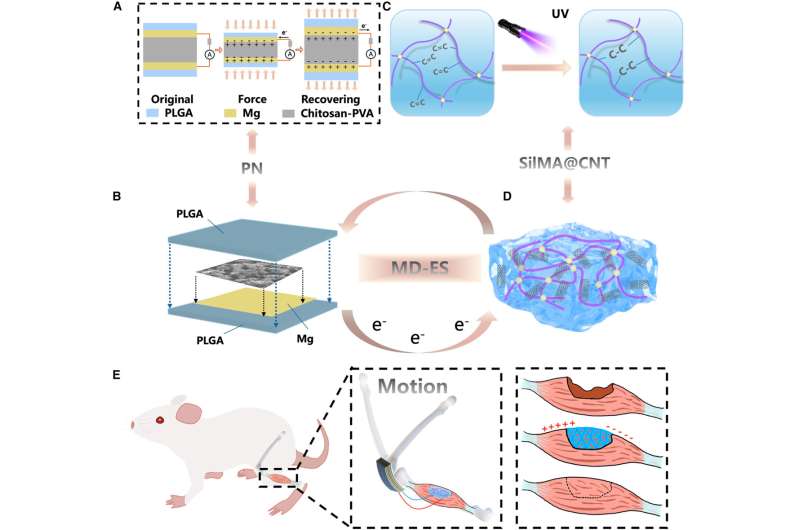
How the MD-ES system works
MD-ES combines degradable materials and in situ electrical stimulation intervention to form a unified implantable strategy. It overcomes key limitations of conventional electrical stimulators—bulkiness, dependence on external power sources, and the need for a secondary surgical procedure to remove the device—which constrain long-term therapeutic outcomes and increase patient morbidity.
The system comprises two core components: a chitosan–polyvinyl alcohol (CS–PVA) composite piezoelectric film unit (PN) and a silk fibroin-based hydrogel scaffold that serves as both an electrical stimulator receiver and tissue engineering scaffold.