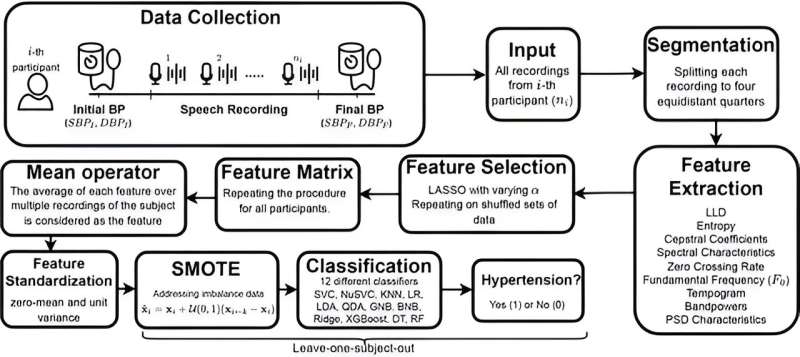
The study’s 245 participants were asked to record their voices up to six times daily for two weeks by speaking into a proprietary mobile app, developed by the Klick scientists, which detected high blood pressure with accuracies up to 84% for females and 77% for males.
The app uses machine learning to analyze hundreds of vocal biomarkers that are indiscernible to the human ear, including the variability in pitch (fundamental frequency), the patterns in speech energy distribution (Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients), and the sharpness of sound changes (spectral contrast).
“By leveraging various classifiers and establishing gender-based predictive models, we discovered a more accessible way to detect hypertension, which we hope will lead to earlier intervention for this widespread global health issue. Hypertension can lead to a number of complications, from heart attacks and kidney problems to dementia,” said Yan Fossat, senior vice president of Klick Labs and principal investigator of the study.