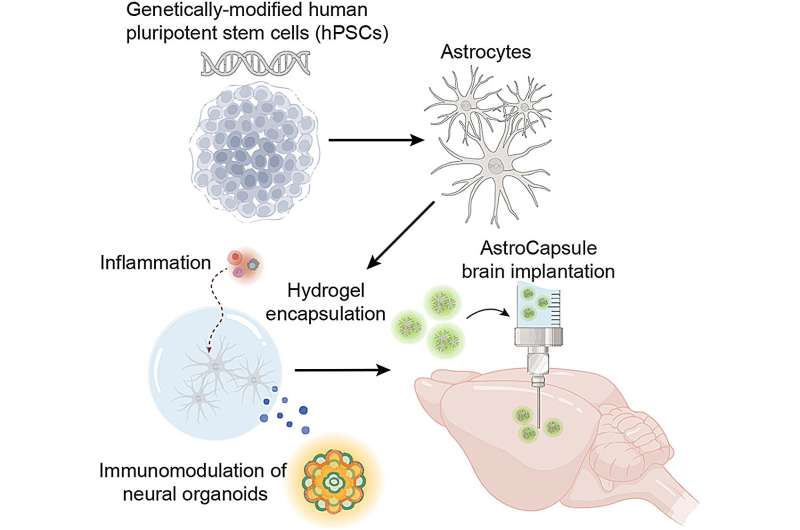
The study, recently published in Biomaterials, was led by Robert Krencik, an associate professor in the Center for Neuroregeneration and Department of Neurosurgery at the Houston Methodist Research Institute. The paper reveals the creation of AstroCapsules, a revolutionary union of bioengineering and neuroscience that encloses human astrocytes (star-shaped, resident brain cells that are crucial to healthy function of the central nervous system) within small biocompatible hydrogel capsules.
The researchers found that when astrocytes within the capsules were armed with a secreted anti-inflammatory protein (interleukin-1 receptor antagonist or IL-1Ra), they could significantly reduce neuroinflammation (measured through inflammatory biomarkers).
Importantly, the AstroCapsules (which are 300 micrometers in diameter—approximately the size of large grains of sand) were confirmed to function when implanted into the brain, showing they could withstand rejection from the body’s immune system. The researchers conducted their research using lab-grown human brain tissue samples, known as organoids, and by using mouse models.