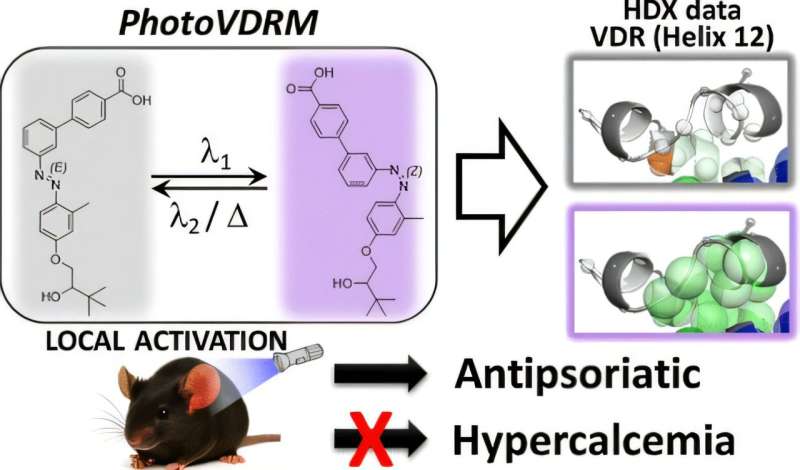
The results, published in the journal ACS Central Science, reinforce the concept that photopharmacology can be applied locally to activate systemically administered drugs. This advance opens the door to targeted and less invasive treatments for skin diseases such as psoriasis.
This work was carried out in collaboration with the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) and the Institute of Neurosciences (UBneuro) of the University of Barcelona, together with two U.S. universities—the Johns Hopkins University and Purdue University—and the pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly and Company.