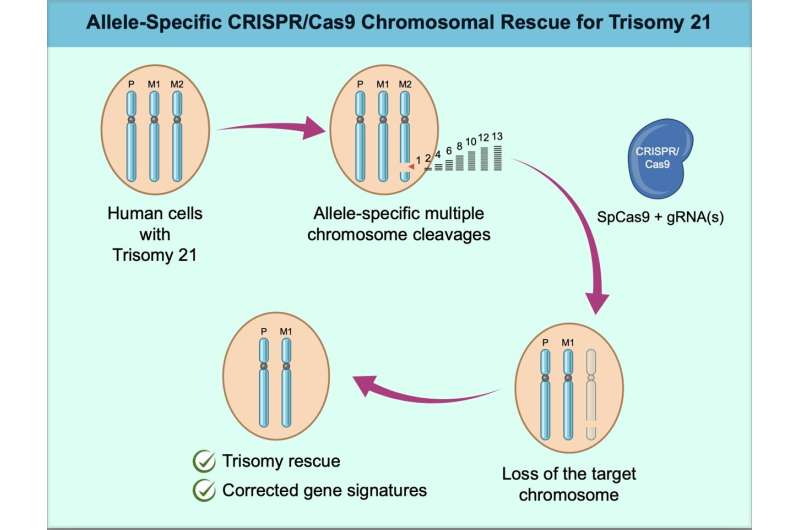
Down syndrome is caused by the presence of a third copy of the 21st chromosome. The condition occurs in approximately 1 in 700 live births and is relatively easy to diagnose at early stages of development. However, there are no treatments.
Ryotaro Hashizume and colleagues used the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing system to cleave the third chromosome in previously generated trisomy 21 cell lines derived from both pluripotent cells and skin fibroblasts. The technique is able to identify which chromosome has been duplicated, which is necessary to ensure the cell does not end up with two identical copies after removal, but instead has one from each parent. The study is published in the journal PNAS Nexus.