Wheezing, a high-pitched whistling sound, is a common indicator of chronic respiratory diseases, including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), due to inflammation and swelling of the airways.
In 2023, nearly nine percent of all adults in the United States had asthma, and COPD remains a leading cause of death in the U.S.
Early detection and management of asthma and COPD is critical. Globally, asthma and COPD are under-diagnosed (20–70% for asthma and up to 81% for COPD). In addition, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that asthma is uncontrolled in 50% of children and 62% of adults, resulting in frequent and intense episodes that can lead to increased emergency department visits and missed school days and workdays.
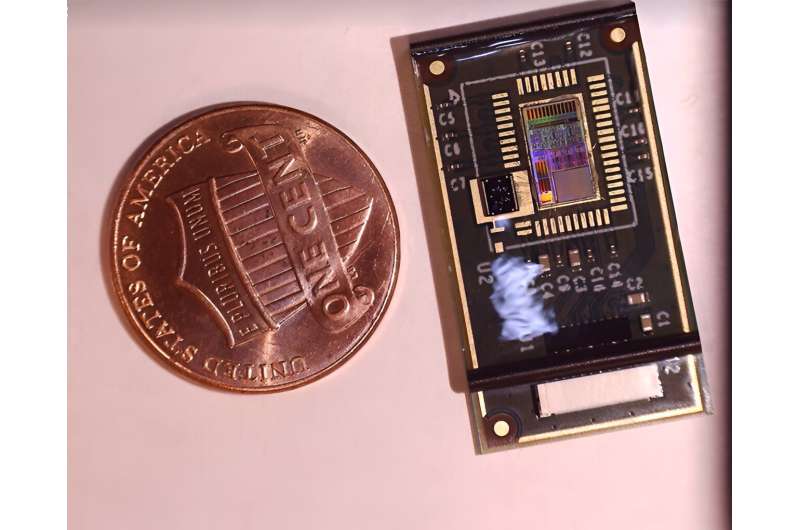
While digital stethoscopes are an improvement over traditional stethoscopes, they pick up airborne noise, which interferes with wheeze detection.
An advanced technological solution is needed that could be used as a screening tool in the clinic and for remote patient monitoring, which would enable physicians to intervene early.