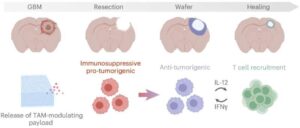
Implantable ‘CANDI’ wafer shows promise for preventing glioblastoma recurrence
Now, researchers have developed a biodegradable implant that can be placed directly into the brain cavity after tumor removal

Now, researchers have developed a biodegradable implant that can be placed directly into the brain cavity after tumor removal
Chromosomal abnormalities—numerical and structural defects in chromosomes—are a common first step in this process, often contributing to normal cells turning cancerous.
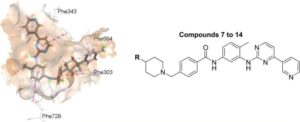
Scientists from King’s College London have successfully applied a new technology that disarms one of the most potent weapons cancer cells use to weaken the effects of chemotherapy drugs.
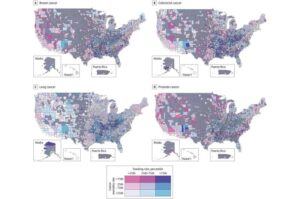
A new study published in JAMA Network Open by the Harvey L. Neiman Health Policy Institute reveals poverty, environmental risks, housing issues, and physical inactivity are top-ranking community-level predictors of disparities in cancer screening, prevalence, and deaths across U.S. counties.
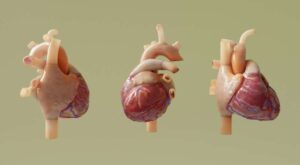
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a cardiac disorder in which the chambers of the heart beat rapidly and irregularly. It’s the most common type of arrhythmia and the leading cardiac cause of stroke.
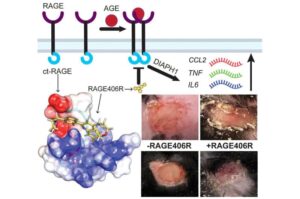
Researchers from the University at Albany and NYU Grossman School of Medicine have found a way to block a key cellular pathway known to drive chronic inflammation and impaired wound healing in people with diabetes.

Doctors may be able to spare patients unnecessarily aggressive breast cancer treatments by collecting and testing cancer cells in patients’ blood, research from the University of Michigan and the University of Kansas suggests.
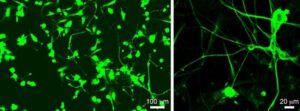
Spinal cord injury (SCI) remains a major unmet medical challenge, often resulting in permanent paralysis and disability with no effective treatments. Now, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have harnessed bioinformatics to fast-track the discovery of a promising new drug for SCI.
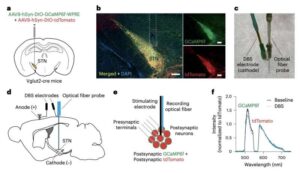
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure that entails the delivery of high-frequency electrical impulses to specific regions of the brain, via surgically implanted electrodes.
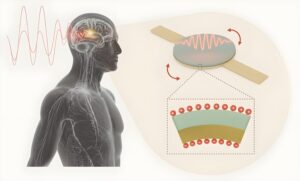
The technology would allow battery-free, minimally invasive, scalable bioelectronic implants such as pacemakers, neuromodulators, and body process monitors.