MedTech News
.................... by Andrew Celentano

AI-powered liquid biopsy can classify pediatric brain tumors with 92% accuracy
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists, in collaboration with scientists at the Hopp Children’s Cancer Center Heidelberg (KiTZ), German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and other international centers, created Methylation-based Predictive Algorithm for CNS Tumors (M-PACT). M-PACT uses AI to sift through ctDNA in cerebrospinal fluid and molecularly classify tumors based on their DNA methylation pattern.
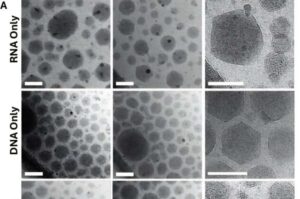
Nanoparticle-based gene editing could expand treatment options for cystic fibrosis
UCLA researchers have developed a lipid nanoparticle-based gene-editing approach capable of inserting an entire healthy gene into human airway cells, restoring key biological function in a laboratory model of cystic fibrosis and establishing a potential new path toward mutation-agnostic gene therapy for inherited lung diseases.
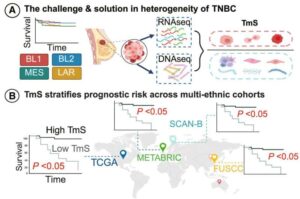
Novel biomarker predicts chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer
Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have developed a new computational approach designed to better account for changes in gene expression within tumors relative to their unique microenvironments. This approach outperformed current methods for predicting chemotherapy response in patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
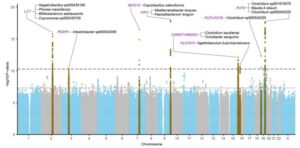
Studies show 11 genetic variants affect gut microbiome
In two new studies on 28,000 individuals, researchers are able to show that genetic variants in 11 regions of the human genome have a clear influence on which bacteria are in the gut and what they do there. Only two genetic regions were previously known. Some of the new genetic variants can be linked to an increased risk of gluten intolerance, hemorrhoids and cardiovascular diseases.
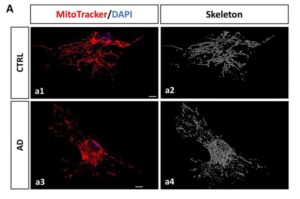
Senescent astrocytes discovered in Alzheimer’s brains point to new treatment targets
Researchers from the NeuroAD group (Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s Disease) within the Department of Cell Biology, Genetics and Physiology at the University of Málaga, also affiliated with IBIMA–BIONAND Platform and CIBERNED, have made a pioneering breakthrough in the fight against this disease by identifying astrocytes as a promising cellular target for the development of future therapies.
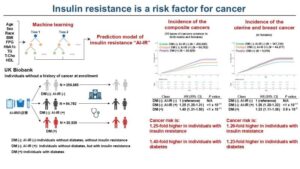
AI model flags insulin resistance as a risk factor for 12 cancers
For the first time, researchers, including those from the University of Tokyo, applied a machine learning-based prediction model of insulin resistance to half a million participants from the UK Biobank and demonstrated that insulin resistance is a risk factor for 12 types of cancer.

A 15-minute VR eye test could flag vision changes tied to brain health
In the recreation room at Eskaton Village in Carmichael, Bonnie Dale, one of the residents, is trying on a virtual reality (VR) headset.
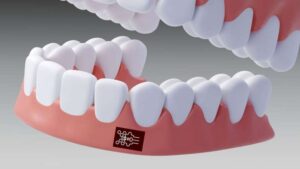
A patch that sticks inside your mouth could spot inflammation early
The specialized sensing layer of the patch targets the tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-⍺) protein, a key biomarker for inflammation.
