MedTech News
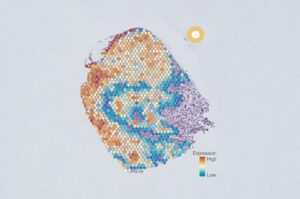
AI tool identifies five distinct cancer cell groups within individual tumors
A multinational team of researchers, co-led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research, has developed and tested a new AI tool to better characterize the diversity of individual cells within tumors, opening doors for more targeted therapies for patients.

Mannkind looks to give those with diabetes another option through inhaled insulin
For those living with diabetes, MannKind offers a very different alternative to the current methods of insulin delivery.
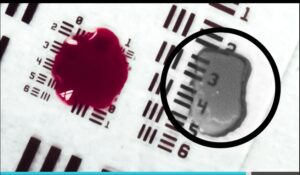
Ocutrx Technologies Inc. Unveils Surgery Breakthrough: First-Ever Technology to Make Blood Translucent During Surgery
IRVINE, Calif. and ABU DHABI, UAE, June 24, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — Ocutrx Technologies Inc. (“Ocutrx”), through its R&D division Genius Labs, today unveiled a major surgical innovation: the ability to render blood translucent in real time during surgery. This patent-pending advancement enables surgeons to see through pooled blood without the need for suction or irrigation—a world first. The technology, called HemoLucence™, will be a feature of the OR-Bot™ 3D Surgical Microscope System, which is scheduled to enter clinical trials in 2025 or 2026.

Cerapedics Announces FDA Approval of PearlMatrix™ P-15 Peptide Enhanced Bone Graft, The First and Only Proven Bone Growth Accelerator for Lumbar Fusion
WESTMINSTER, Colo., June 23, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — Cerapedics Inc., a global, commercial-stage orthopedics company dedicated to redefining the path to bone repair, today announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) premarket approval (PMA) of PearlMatrix™ P-15 Peptide Enhanced Bone Graft as a Class III drug-device combination product for use in single-level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) surgery in adult patients with degenerative disc disease (DDD). Despite the availability of over 350+ spinal bone grafts, none have demonstrated a substantial improvement in fusion speed until now. Powered by a proprietary P-15 Osteogenic Cell Binding Peptide, PearlMatrix Bone Graft is the first and only bone growth accelerator (BGA) proven to accelerate lumbar fusion.
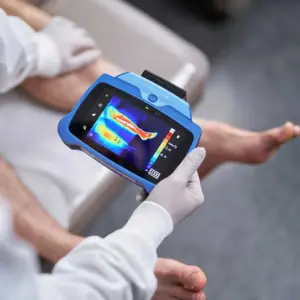
MolecuLight Unveils Advanced Multimodal Imaging with Thermal Capabilities at St. Louis Wound & Vascular Symposium
New imaging innovation enhances wound assessment by combining fluorescence and thermal data for improved diagnostic precision and patient care

Meril Launches MyClip, India’s First Transcatheter-Edge-to-Edge Repair (TEER) System for Treatment of Severe Mitral Regurgitation
Meril Life Sciences, a leading global med-tech company, marked a significant milestone with the launch of MyClip, India’s first Transcatheter Edge-To-Edge Repair (TEER) system, on June 14
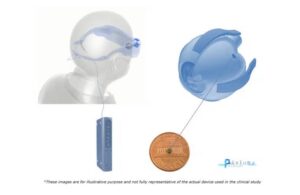
Science submits BCI for vision restoration for CE mark
Brain-computer interface (BCI) developer Science Corporation today said it submitted its Prima retinal implant for CE mark approval.
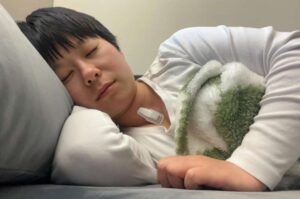
Stick-on sleep monitor promises smarter, more accurate detection of sleep disorders
A team of Northwestern investigators have developed a wearable and wireless sleep monitoring device that provides an in-depth analysis of different sleep stages and may improve the detection of sleep disorders, detailed in a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
