MedTech News
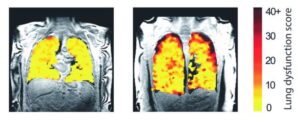
New lung scanning method can show treatment effects in real time
A new method of scanning lungs is able to show the effects of treatment on lung function in real time and enable experts to see the functioning of transplanted lungs. This could enable medics to identify any decline in lung function sooner.
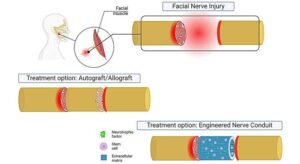
Engineering a smile: Stem cell–based conduits restore facial nerve function in animal study
A gesture as simple as a smile can often convey what words cannot. This is part of why nonverbal communication is so central to human interaction. It is also why facial nerve disorders and injuries can be devastating.
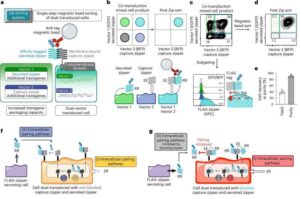
Engineered T cells could help patients overcome resistance to CAR T cell therapy
Physician-researchers with City of Hope have developed a way to add features to T cells to help them overcome mechanisms of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy resistance. Their new system is outlined in a paper published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
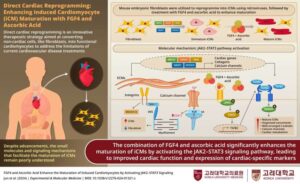
Reprogramming cells for heart repair: New method transforms ordinary fibroblasts into mature cardiomyocytes
Cardiovascular disease continues to lead as the primary cause of death across the globe, taking millions of lives every year. Damage caused by these diseases is particularly difficult to repair, since the heart has minimal ability to regenerate itself. But what if we could reprogram the body’s own cells to restore damaged tissue? This question has been tackled by scientists at Korea University, led by Dr. Myeong-Hwa Song.
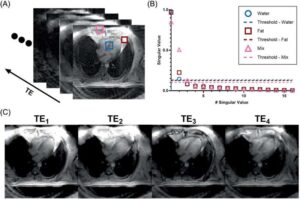
New MRI technique identifies heart disease risk from fat composition
Everyone knows the health risks of carrying too much fat around the waist and hips, but UVA Health scientists are developing a noninvasive way to assess the health risks of unseen fat around the heart.
More blood transfusions linked to lower 6-month mortality in heart-attack patients with anemia
Giving more blood to anemic patients after a heart attack may save lives, according to a Rutgers Health–led study. The study, published in NEJM Evidence, affirms research conducted in 2023 that suggested mortality rate or recurrent heart attacks were more frequent in anemic patients who received less blood.
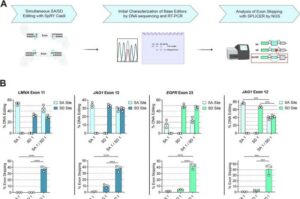
Gene editing tool reduces Alzheimer’s plaque precursor in mice
A new gene editing tool that helps cellular machinery skip parts of genes responsible for diseases has been applied to reduce the formation of amyloid-beta plaque precursors in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign report.
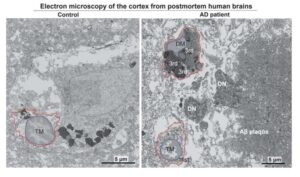
Alzheimer’s progression tied to stress-induced microglial lipid release
Researchers with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have unveiled a critical mechanism that links cellular stress in the brain to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
