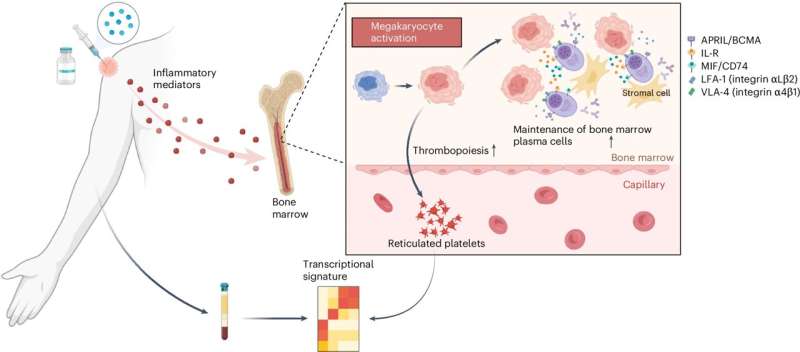
Scientists have long been stymied by why some vaccines can coax the body to produce antibodies for decades, while others last mere months. Now, a study led by researchers at Stanford Medicine has shown that variation in vaccine durability can, in part, be pinned on a surprising type of blood cell called megakaryocytes, typically implicated in blood clotting.
“The question of why some vaccines induce durable immunity while others do not has been one of the great mysteries in vaccine science,” said Bali Pulendran, Ph.D., a professor of microbiology and immunology.
“Our study defines a molecular signature in the blood, induced within a few days of vaccination, that predicts the durability of vaccine responses and provides insights into the fundamental mechanisms underlying vaccine durability.”