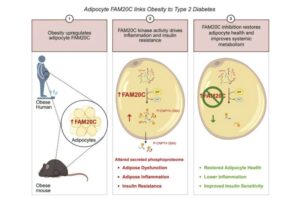
Blocking gene improves metabolic health in obese mice without weight loss
Weill Cornell Medicine investigators have identified an early step in a cellular process that leads to inflammation in fat cells and may result in type 2 diabetes in people with obesity.