MRI antenna can boost image quality and shorten scan times—without changing existing machines
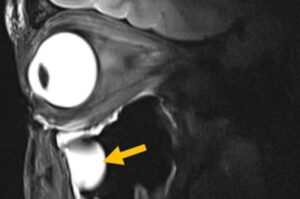
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of medicine’s most powerful diagnostic tools. But certain tissues deep inside the body—including brain regions and delicate structures of the eye and orbit that are of particular relevance for ophthalmology—are difficult to image clearly. The problem is not the scanner itself, but the hardware that sends and receives radio signals.