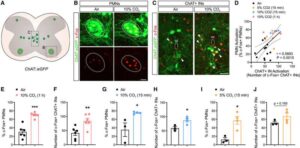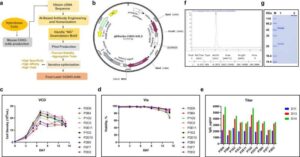
Novel monoclonal antibody targets deadly sepsis by preventing ‘cytokine storms’
Scientists at the University of Virginia School of Medicine and the University of Michigan have developed a monoclonal antibody to stop sepsis, a deadly full-body infection.