HR HealthCare Expands EZ Series Portfolio with EZ Protect Hydrophilic Closed System Intermittent Catheter Line
New product line extends options to better meet patient needs

New product line extends options to better meet patient needs

LifeVac is approved for use as a single-use, non-powered, non-invasive airway clearance device.
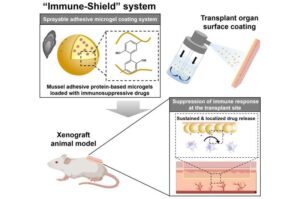
A new technology has been developed to suppress immune rejection, the biggest challenge in organ transplantation, without causing systemic side effects.
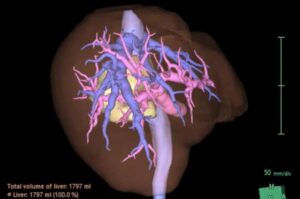
Researchers at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine now show that it is possible to remove the caudate lobe safely using a surgical robot, even in an older patient, and still remove the cancer completely.
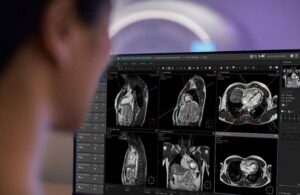
Philips (NYSE: PHG)+ announced today that it received FDA 510(k) clearance for its SmartHeart planning solution.

A machine-learning model developed by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators may provide clinicians with an early warning of a complication that can occur late in pregnancy.
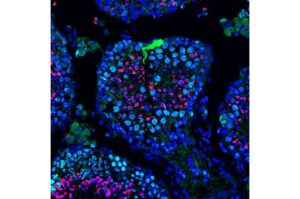
Researchers have found that targeted delivery of messenger RNA (mRNA) can restore sperm production and fertility in genetically infertile male mice.
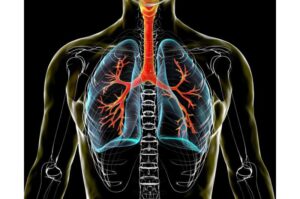
Findings from a study led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center–Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC–James) support the potential of new therapies that could improve clinical outcomes for patients with squamous and adenocarcinoma non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) that don’t respond to immunotherapy.
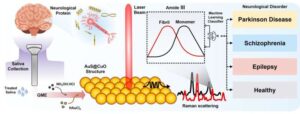
A team of Korean researchers has, for the first time, developed a technology capable of enabling early diagnosis of major neurological disorders including epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and schizophrenia using only a small amount of saliva
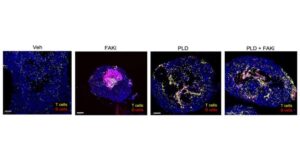
Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys and the University of California San Diego have published findings in Cell Reports demonstrating a treatment approach in mice that allowed more tumor-fighting cells to approach tumors.