
Pulse wins IDE approval
Pulse Biosciences will study PFA in cardiac surgery. Meanwhile, Galvanize Therapeutics also named a new CEO, and PFA pioneer Steven Mickelsen has launched another company.

Pulse Biosciences will study PFA in cardiac surgery. Meanwhile, Galvanize Therapeutics also named a new CEO, and PFA pioneer Steven Mickelsen has launched another company.
The finding opens a new path for cancer treatment.
The current step represents a major proof of concept in humans for TruLeaf’s innovative technology aimed at transcatheter replacement of the mitral and tricuspid valves
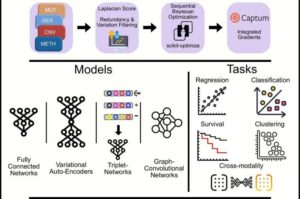
Nearly 50 new cancer therapies are approved every year. This is good news. “But for patients and their treating physicians, it is becoming increasingly difficult to keep track and to select the treatment methods from which the people affected—each with their very individual tumor characteristics—will benefit the most,” says Dr. Altuna Akalin, head of the Bioinformatics and Omics Data Science technology platform at the Berlin Institute for Medical Systems Biology of the Max Delbrück Center (MDC-BIMSB).
Researchers at Emory Goizueta Brain Health Institute and partner institutions have found new clues in the blood that could help explain why Alzheimer’s disease develops and how it affects memory.
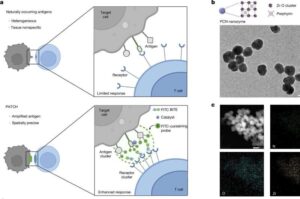
Tumor immunotherapies, especially those leveraging T-cells to identify and eliminate cancer cells, represent a major breakthrough in cancer treatment. However, many tumor-associated antigens are not expressed at a high enough density on the cancer cell surface to effectively activate T-cells, and these antigens are often present at low levels in normal tissues, leading to poor treatment specificity and potential off-target toxic side effects.
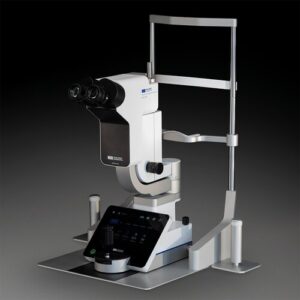
MASON, Ohio, Sept. 12, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — Haag-Streit USA, a leading manufacturer and distributor of ophthalmic diagnostic devices, surgical microscopes, and virtual reality-based medical simulators, is proud to announce the launch of two new innovations: the Elara 900 and the Refractor 900. Both products will make their international debut at ESCRS 2025 in Copenhagen and their US debut at the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) annual meeting in October.

Pulnovo Medical announced today that it received two FDA investigational device exemption (IDE) approvals for its technology.
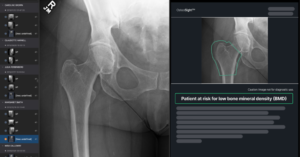
Naitive Technologies, a medical technology company developing AI-driven software to reimagine orthopedic care has announced that it has received 510(k) clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its flagship product, OsteoSight. OsteoSight enables opportunistic assessment of bone mineral density (BMD) using standard X-rays acquired to investigate other clinical concerns, such as pain associated with arthritis or a fall.

Advance from SMART will help to better identify disease markers and develop targeted therapies and personalized treatment for diseases such as cancer and antibiotic-resistant infection.