For the First Time, Lab‑Grown Brain Organoids Display Ability to Learn
Learn more about the advances in brain organoids and what this science could mean for the future.

Learn more about the advances in brain organoids and what this science could mean for the future.
Research reveals how cells may activate a compensation system that can reduce the effects of harmful genetic mutations. This could inform gene therapy development.
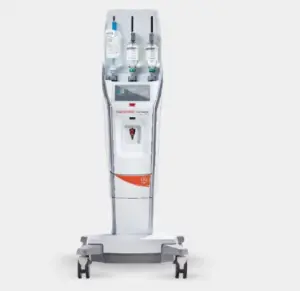
The FDA’s expanded clearances broaden the application of Bayer’s Medrad MRXperion system across a wider range of MR settings.
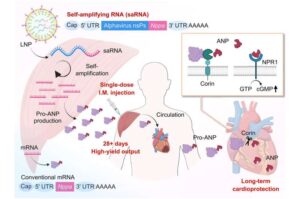
This simple injection may one day help people recover more safely and fully after a heart attack.
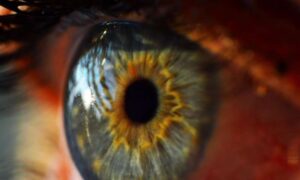
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers have developed an early-stage, experimental “living eye drop” that uses naturally occurring eye bacteria to support corneal wound healing.
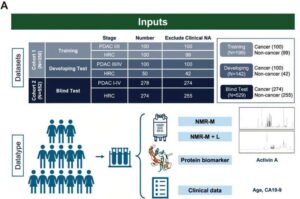
A team of researchers from Taiwan has developed PanMETAI, an AI-powered platform that analyzes metabolic fingerprints in a simple blood sample to detect pancreatic cancer at its earliest stages—when treatment is most effective—achieving up to 94% diagnostic accuracy.
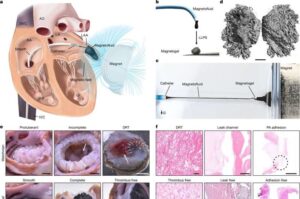
Researchers have developed a promising new treatment involving magnetic fluids.
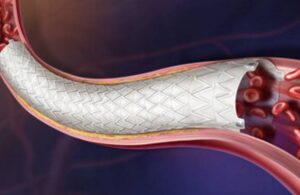
BD (NYSE: BDX)+ announced today that it received CE mark approval for its Revello vascular covered stent system.

Washington State University researchers have developed a 3D-printed model of the left side of the heart that contracts and beats, offering the chance for surgeons and medical students to rehearse important heart surgeries on a model that acts like the real thing.

Wearable sensors may help identify people with multiple sclerosis (MS) who are more likely to have worsening disability and loss of brain volume, according to a study published in Neurology.