Laser Therapy Boosts Survival in Treating Brain Cancer, With Nearly Half Alive at 18 Months
Learn how a new laser-based therapy is giving patients with aggressive brain cancer a stronger chance at survival.

Learn how a new laser-based therapy is giving patients with aggressive brain cancer a stronger chance at survival.
Learn more about Pico-C, a tool that helps reveal the genome’s structure during the first days of life.
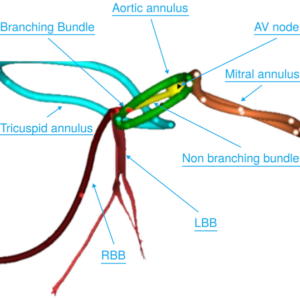
TORTOLA, British Virgin Islands, Feb. 25, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — Cara Medical Ltd. today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted 510(k) clearance for the CARA System, a computed tomography angiography (CTA)-based platform that provides noninvasive, patient-specific three-dimensional (3D) visualization of the cardiac conduction system.
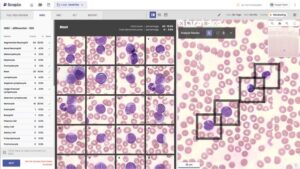
PARSIPPANY, N.J., Feb. 25, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — Scopio Labs today announced it has achieved IVDR certification from BSI, a major regulatory milestone that clears the path for its AI-driven digital morphology platforms in the European Union
ZURICH, Feb. 25, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — Polaroid Therapeutics (PTx) today announces that POLTX_Fiber™ has received the CE Mark as a Class IIb medical device with APT™ (Antimicrobial Polymer Technology).

DALLAS, Feb. 25, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — 4WEB Medical, an orthopedic implant company focused on developing innovative implants that utilize its proprietary TRUSS Implant Technology™, announced that it has received 510(k) clearance to market its SI Joint Truss System™.
As people age, it becomes harder to know who is on track for healthy years ahead and who may be at higher risk for serious decline. A new study suggests that part of the answer may already be circulating in the bloodstream.
Learn how reseachers are working to engineer certain bacteria to consume tumors.

Medtronic (NYSE:MDT) announced today that it launched its MiniMed Go smart multiple daily injection (MDI) system with the Simplera sensor.
Carea, a pregnancy and postnatal wellbeing app, is bridging this gap with the launch of its new Trying to Conceive: IVF/IUI Mode, to support the tens of thousands of women undergoing complex fertility treatment, amid growing concern over inconsistent clinic continuity and limited day-to-day guidance.