
WashU Medicine introduces new blood test for Alzheimer’s symptom timing
Researchers analysed data from two Alzheimer’s cohorts.

Researchers analysed data from two Alzheimer’s cohorts.
Medtronic (NYSE: MDT)+ announced today that it received CE mark for its ColonPRO fourth-generation software for AI-assisted colonoscopy.
Biotronik announced today that it received FDA approval for its Solia CSP S pacing lead for left bundle branch area pacing (LBBAP).

Allurion Technologies (NYSE:ALUR) announced today that the FDA granted premarket approval (PMA) for its Allurion Gastric Balloon System.
A protein lurking around in the blood can help with the accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. In a recent study, researchers from Spain investigated how blood-based biomarkers, such as a protein called p-tau217, affect both the clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s and neurologists’ confidence in their diagnosis.
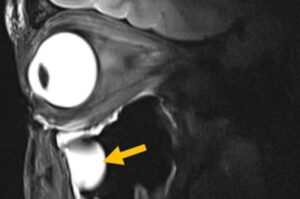
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of medicine’s most powerful diagnostic tools. But certain tissues deep inside the body—including brain regions and delicate structures of the eye and orbit that are of particular relevance for ophthalmology—are difficult to image clearly. The problem is not the scanner itself, but the hardware that sends and receives radio signals.
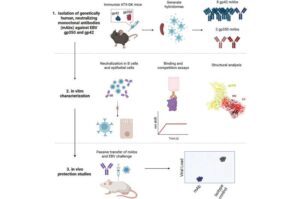
Fred Hutch Cancer Center scientists reached a crucial milestone in blocking Epstein Barr virus (EBV), a pathogen estimated to infect 95% of the global population that is linked to multiple types of cancer, neurodegenerative diseases and other chronic health conditions. Using mice with human antibody genes, the research team developed new genetically human monoclonal antibodies that prevent two key antigens on the surface of the virus from binding to and entering human immune cells.

Medtronic is investing in the rollout of the Symplicity Spyral renal denervation procedure, including hiring for new market development roles, CEO Geoff Martha said on an earnings call.

The company has integrated its Eversense 365 implant with Sequel Med Tech’s insulin delivery system to automate the management of Type 1 diabetes.
Medtronic continues to expand the growth opportunities for its hypertension-treating Symplicity Spyral renal denervation system.