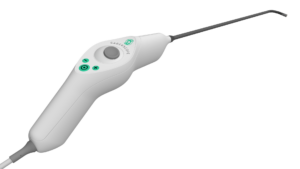
Xenocor Announces FDA Clearance of Saberscope®, the First Single-Use 5mm Articulating Laparoscope for Enhanced Surgical Visualization
SALT LAKE CITY, Feb. 24, 2026 /PRNewswire/ — Xenocor, Inc. today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared the new Xenocor Saberscope®, a single-use 5mm articulating laparoscope designed for high definition (HD) visualization during minimally invasive abdominal (belly) and thoracic (chest) surgical procedures.