AI tool debuts with better genomic predictions and explanations
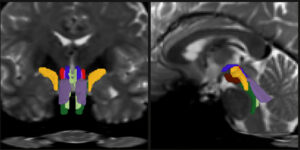
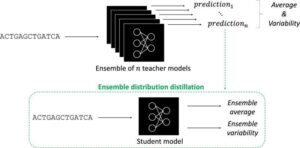
Artificial intelligence has taken the world by storm. In biology, AI tools called deep neural networks (DNNs) have proven invaluable for predicting the results of genomic experiments. Their usefulness has these tools poised to set the stage for efficient, AI-guided research and potentially lifesaving discoveries—if scientists can work out the kinks. The findings are published in the journal npj Artificial Intelligence.